

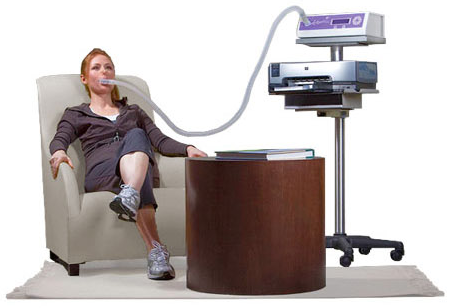
VO₂ Max Testing
VO2MAX: 45-60 MINS
(includes pre and post test preparations, actual test varies between 5mins to 20 mins depending on endurance of person)
What is a VO2 Max Test?

A VO2 Max Test is a measurement that reflects a person’s ability to perform sustained exercise. It is generally considered the best indicator of cardiovascular fitness and aerobic endurance. The actual measurement is “milliliters of oxygen used in one minute per kilogram of body weight.” It is suitable for a wide range of individuals, from the sedentary to elite athletes.
Why Test VO2 Max?
A complete VO2 Fitness test can give trainers and clients the tools to set realistic goals and assess improvement. Studies show that previously sedentary people training at 75% of aerobic power for 30 minutes, 3 times a week over 6 months increase VO2 Max an average of 15-20%. Many people are inefficient exercisers, with no understanding of what specific heart rate, intensity or duration would best help them reach their specific goals such as fat burning, endurance training, or cardio conditioning. An initial VO2 Max test can clarify the specific target heart rates that will enable each individual to reach their fitness goals more effectively, with less fatigue and fewer injuries. Periodic retesting provides motivating feedback as the fitness program progresses.
The test also determines the number of calories burned during every level of exercise, providing valuable information when designing a weight loss program. And if CO2 is measured during the test, a Respiratory Exchange Ratio (RER) can determine the proportion of energy coming from carbohydrates and fats at various levels of exercise intensity. Since physical conditioning and exercise intensity affect these proportions, this information can be very helpful when designing a workout intended to burn fat.
VO2 Max testing is a valuable tool for serious athletes to assess performance and evaluate training regimens. Even though extensive training can sometimes cause an athlete to reach a plateau in VO2 Max, he can still use his VO2 Max test results to make further improvements in performance. This is accomplished as he pushes to increase anaerobic threshold (AT) and maintain that threshold for longer periods of time. This enhances both endurance and cardiovascular performance.
How is VO2 Max Measured?
VO2 Max is the maximum rate of oxygen consumption that can be attained during the most intense exercise possible. The measurement requires that the subject breathe into an oxygen consumption analyzer during an all-out effort (usually on a treadmill or bicycle) as part of a graded exercise protocol. These protocols involve specific increases in the speed and intensity of the exercise. While exercising, the person wears a mask to collect all the air he breathes in and out for a measurement of the volume of exhaled gas and the concentration of oxygen in that exhaled gas. This determines how much oxygen is used during each minute of the exercise test.
A person’s oxygen consumption rises in a linear relationship with exercise intensity — up to a point. There are specific physiological markers (AeT, AT) that can be detected throughout the test as oxygen consumption is measured. Eventually, oxygen consumption plateaus even if the exercise intensity increases. When the person is no longer able to keep up with the oxygen demands of his muscles and complete fatigue forces him to stop exercising, then his oxygen consumption has reached a maximum, and VO2 Max can be calculated. The test usually takes between 10 and 15 minutes.
RESTING METABOLIC RATE
What is Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)?
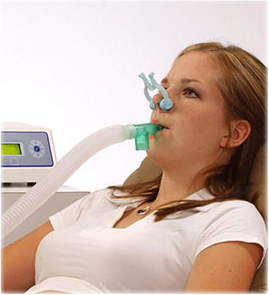
Metabolism, quite simply, is the conversion of food to energy.
Metabolic rate is a measure of how much food, or fat, is converted to energy in a day. Resting metabolic rate (RMR) is the measurement of how much food, or energy, is required to maintain basic body functions such as heartbeat, breathing, and maintenance of body heat while you are in a state of rest. That energy is expressed in calories per day. So an RMR test shows how many calories you burn at rest, doing nothing more than sitting in a chair.
How Does Metabolic Testing Work?
Indirect calorimetry (a measurement of metabolic rate) relies on the fact that burning 1 calorie (Kilocalorie) requires 208.06 milliliters of oxygen. Because of this very direct relationship between caloric burn and oxygen consumed, measurements of oxygen uptake (VO2) and caloric burn rate are virtually interchangeable.
Oxygen uptake requires a precise measurement of the volume of expired air and of the concentrations of oxygen in the inspired and expired air. The process requires that all of the air a person breathes out be collected and analyzed while they rest quietly. The KORR™ indirect calorimeters contain a precision air flow sensor that measures the volume of expired air, and an oxygen sensor that measures the concentration of oxygen. Once the factors of humidity, temperature and relative humidity are accounted for, the KORR™ instrument provides the most accurate results available in a compact metabolic analyzer.
Why Test RMR to Treat Obesity?
Proof of “normal” metabolism
Most overweight people are convinced they have a slow metabolism. The truth is that statistically, most overweight and obese individuals have average or higher than average metabolic rates. Taking a measurement removes this excuse. Seeing that their bodies can indeed burn calories can be very encouraging and motivating.
Stabilize weight loss
Regardless of the method used to lose weight, a patient’s RMR will decrease after weight loss. The decrease is actually below the level predicted by fat-free mass (FFM). Although the cause is unclear, it appears that in most cases, if a patient can maintain his new weight for 6 months, his RMR will eventually rise to the expected level. Pinpointing the precise number of calories necessary to maintain is key to surviving this crucial period.
Pinpoint caloric weight loss zone
When restricting calories, knowing a baseline RMR is invaluable. KORR Metabolic Analyzers calculate a “weight loss zone” for 1 ½ pound a week weight loss, or practitioners can use the RMR to calculate a caloric goal unique for their patients.
Detection and Diagnosis of hypo-metabolism
In cases where a patient has a clinically low metabolic rate, further diagnosis and treatment by a physician will be required before successful weight loss can be achieved.
Assess the effect of weight loss treatment on metabolism
Once calories are restricted, medications are introduced, or an exercise plan has been implemented, the human body will respond. This is especially true of significant interventions, such as bariatric surgery. The caloric goals of a dietary plan will rarely sustain a patient throughout an entire weight loss regimen. The result is the dreaded “plateau.” Periodic assessment of RMR will show the effects of the treatments and allow adjustments to the caloric goals.
























